A Cognitive Framework for Self-Adjusting Systems Through Experience Feedback
agentic Experience Architecture. the real power of agents
Evolution of Agentic Architectures
Evolution of Agentic Architectures
Evolution of Agentic Architectures
In traditional AI architectures, agents are defined by tasks or roles.
In AEA, agents are defined by journeys — the sequences of intent, context, and interaction that users actually live through.



Evolution Timeline of Agentic Architectures
2020 – 2022
Task-Based & Role-Based Decomposition
2022 – 2024
Tool-Oriented & Plan-and-Execute Architectures
2024 – 2025
Journey-Based Architectures
2026 +
Context Aware Agentic Experience Architecture (AEA)
Evolution Timeline of Agentic Architectures
2020 – 2022
Task-Based & Role-Based Decomposition
2022 – 2024
Tool-Oriented & Plan-and-Execute Architectures
2024 – 2025
Journey-Based Architectures
2026 +
Context Aware Agentic Experience Architecture (AEA)
Evolution Timeline of Agentic Architectures
2020 – 2022
Task-Based & Role-Based Decomposition
2022 – 2024
Tool-Oriented & Plan-and-Execute Architectures
2024 – 2025
Journey-Based Architectures
2026 +
Context Aware Agentic Experience Architecture (AEA)
Where Does AEA Fit Best?
Where Does AEA Fit Best?
Where Does AEA Fit Best?
AEA should be applied where intelligence and experience must co-evolve — where reasoning needs to stay human-understandable, adaptive, and explainable in real time
AEA should be applied where intelligence and experience must co-evolve — where reasoning needs to stay human-understandable, adaptive, and explainable in real time
AEA should be applied where intelligence and experience must co-evolve — where reasoning needs to stay human-understandable, adaptive, and explainable in real time



Metrics That Signal Readiness
Metrics That Signal Readiness
Metrics That Signal Readiness



A practical blueprint
A practical blueprint
A practical blueprint
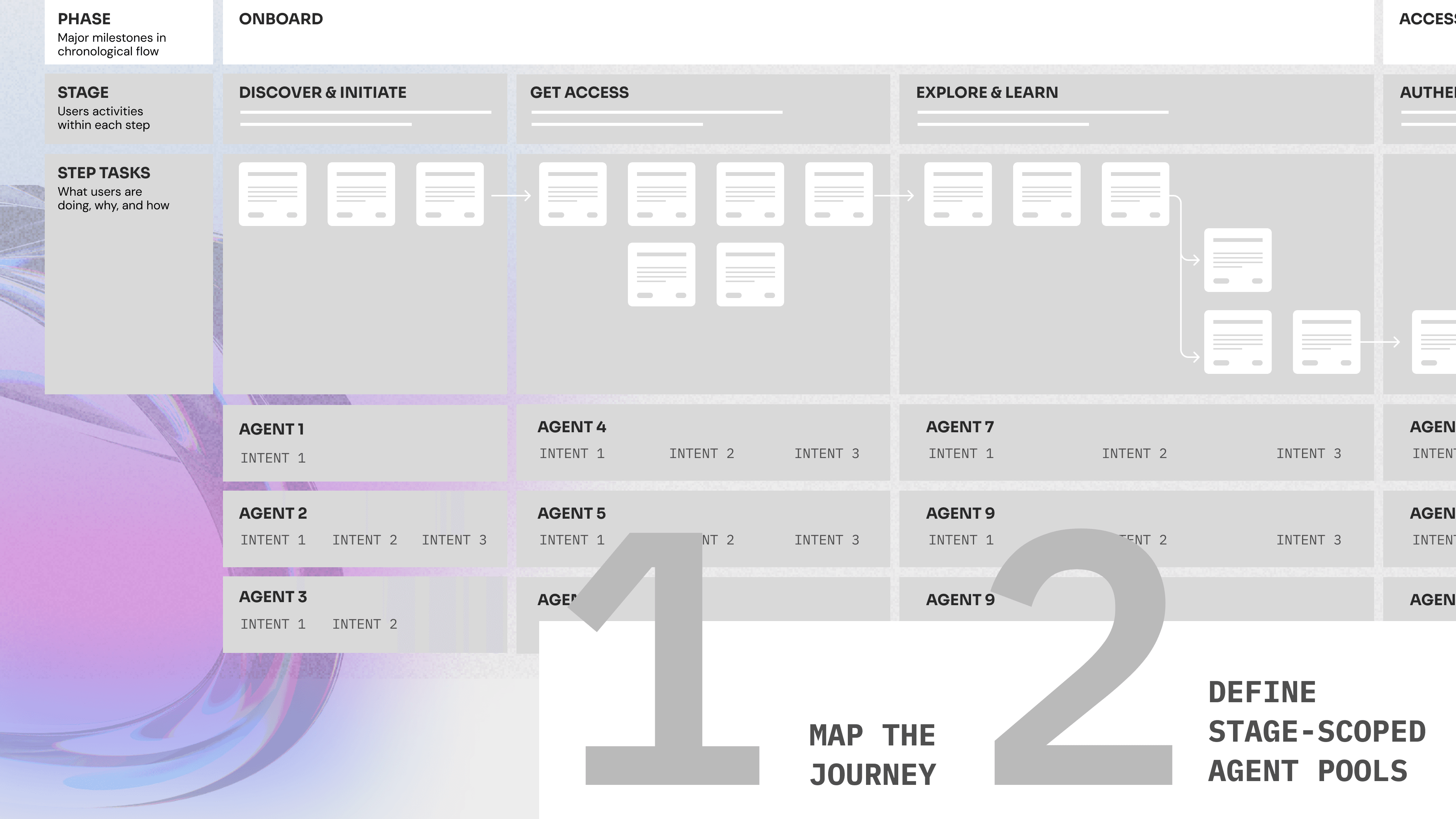





INSIGHTS GAINED BASED ON ROUTER AND ORCHESTRATOR SEPARATION
Insights gained:
Which stage consistently delays the journey
Which routing policies cause loops or misfires
Which agent pool performs best under which signals
This enables micro-level optimization — not just global tuning.
Strategic Insights — “Where to invest optimization effort?”
The separation creates two optimization surfaces:
Orchestrator layer: journey design, global policy, loop strategy
Stage router layer: local reasoning, agent selection, efficiency


What is difficult here and what to do
Cache correctness & invalidation
Why hard: Identical-looking requests aren’t identical (doc updates, policy changes, model/prompt version drift). Silent stale hits = wrong answers.
Do this: Content-addressed keys (hash docs, prompts, model IDs, policy bundle, user scope), TTL + freshness cutoffs, lineage tracking, and explicit bust rules (e.g., “if corpus updated after X, bypass verify-node cache”). Add canaries: 1–5% of hits recompute and compare.
Cache correctness & invalidation
Why hard: Identical-looking requests aren’t identical (doc updates, policy changes, model/prompt version drift). Silent stale hits = wrong answers.
Do this: Content-addressed keys (hash docs, prompts, model IDs, policy bundle, user scope), TTL + freshness cutoffs, lineage tracking, and explicit bust rules (e.g., “if corpus updated after X, bypass verify-node cache”). Add canaries: 1–5% of hits recompute and compare.
Cache correctness & invalidation
Why hard: Identical-looking requests aren’t identical (doc updates, policy changes, model/prompt version drift). Silent stale hits = wrong answers.
Do this: Content-addressed keys (hash docs, prompts, model IDs, policy bundle, user scope), TTL + freshness cutoffs, lineage tracking, and explicit bust rules (e.g., “if corpus updated after X, bypass verify-node cache”). Add canaries: 1–5% of hits recompute and compare.
Policy & PII propagation
Why hard: Stage-specific access rules/PII handling shift; a cached artifact might violate today’s policy.
Do this: Include a policies_hash in every cache key; bump on any policy change. Enforce policy checks at read time (gate access by user/tier) and prefer recompute over reuse when policies tighten.
Policy & PII propagation
Why hard: Stage-specific access rules/PII handling shift; a cached artifact might violate today’s policy.
Do this: Include a policies_hash in every cache key; bump on any policy change. Enforce policy checks at read time (gate access by user/tier) and prefer recompute over reuse when policies tighten.
Policy & PII propagation
Why hard: Stage-specific access rules/PII handling shift; a cached artifact might violate today’s policy.
Do this: Include a policies_hash in every cache key; bump on any policy change. Enforce policy checks at read time (gate access by user/tier) and prefer recompute over reuse when policies tighten.
Stable contracts between nodes
Why hard: Small schema changes break downstream agents or make caches unusable.
Do this: JSON Schema per node I/O, semantic versioning (node@v3), adapters for N–1 versions, and contract tests in CI that replay real traces.
Stable contracts between nodes
Why hard: Small schema changes break downstream agents or make caches unusable.
Do this: JSON Schema per node I/O, semantic versioning (node@v3), adapters for N–1 versions, and contract tests in CI that replay real traces.
Stable contracts between nodes
Why hard: Small schema changes break downstream agents or make caches unusable.
Do this: JSON Schema per node I/O, semantic versioning (node@v3), adapters for N–1 versions, and contract tests in CI that replay real traces.
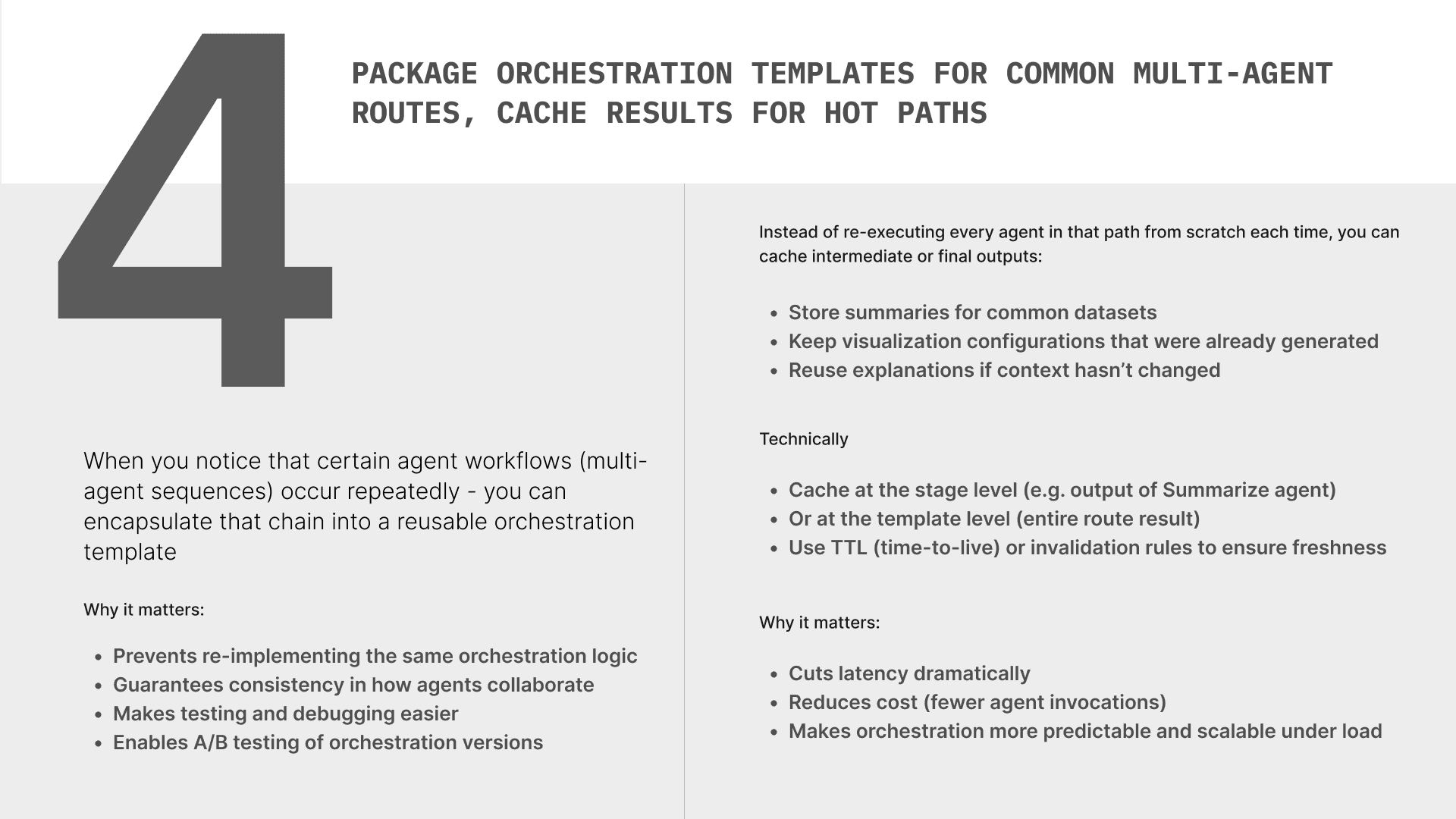
Discovering the right templates (not overfitting)
Why hard: Early templates can ossify incidental flows; you cache the wrong thing.
Do this: Mine routing logs → cluster common DAGs → require minimal success/volume thresholds before templating. Review monthly; retire low-hit templates. Keep a “sandbox template” bucket for experimentation.
Discovering the right templates (not overfitting)
Why hard: Early templates can ossify incidental flows; you cache the wrong thing.
Do this: Mine routing logs → cluster common DAGs → require minimal success/volume thresholds before templating. Review monthly; retire low-hit templates. Keep a “sandbox template” bucket for experimentation.
Discovering the right templates (not overfitting)
Why hard: Early templates can ossify incidental flows; you cache the wrong thing.
Do this: Mine routing logs → cluster common DAGs → require minimal success/volume thresholds before templating. Review monthly; retire low-hit templates. Keep a “sandbox template” bucket for experimentation.
Determinism vs. model variance
Why hard: Non-deterministic outputs (temperature, time in prompt) ruin cache keys and reproducibility.
Do this: Temperature = 0 (or fixed seed) for cacheable nodes, freeze prompts and hash them, avoid time-dependent phrasing, and separate “creative” nodes (no cache) from “computational” nodes (cache).
Determinism vs. model variance
Why hard: Non-deterministic outputs (temperature, time in prompt) ruin cache keys and reproducibility.
Do this: Temperature = 0 (or fixed seed) for cacheable nodes, freeze prompts and hash them, avoid time-dependent phrasing, and separate “creative” nodes (no cache) from “computational” nodes (cache).
Determinism vs. model variance
Why hard: Non-deterministic outputs (temperature, time in prompt) ruin cache keys and reproducibility.
Do this: Temperature = 0 (or fixed seed) for cacheable nodes, freeze prompts and hash them, avoid time-dependent phrasing, and separate “creative” nodes (no cache) from “computational” nodes (cache).
Observability you actually use
Why hard: Without per-node hit/miss, you can’t tune ROI or catch drift.
Do this: Log per-node {hit|miss, latency_saved_ms, tokens_saved, confidence, upstream_keys}; build a tiny dashboard with hit-rate by node and p95 latency deltas. Alert on sudden hit-rate drops or rising recompute variance.
Observability you actually use
Why hard: Without per-node hit/miss, you can’t tune ROI or catch drift.
Do this: Log per-node {hit|miss, latency_saved_ms, tokens_saved, confidence, upstream_keys}; build a tiny dashboard with hit-rate by node and p95 latency deltas. Alert on sudden hit-rate drops or rising recompute variance.
Observability you actually use
Why hard: Without per-node hit/miss, you can’t tune ROI or catch drift.
Do this: Log per-node {hit|miss, latency_saved_ms, tokens_saved, confidence, upstream_keys}; build a tiny dashboard with hit-rate by node and p95 latency deltas. Alert on sudden hit-rate drops or rising recompute variance.
Versioning & rollout safety
Why hard: Changing any piece (template, model, prompt) can shatter caches or degrade answers.
Do this: Treat templates like code: PRs, review, A/B at template version granularity, blue/green enablement, and quick rollback. Keep old caches warm for one version overlap.
Versioning & rollout safety
Why hard: Changing any piece (template, model, prompt) can shatter caches or degrade answers.
Do this: Treat templates like code: PRs, review, A/B at template version granularity, blue/green enablement, and quick rollback. Keep old caches warm for one version overlap.
Versioning & rollout safety
Why hard: Changing any piece (template, model, prompt) can shatter caches or degrade answers.
Do this: Treat templates like code: PRs, review, A/B at template version granularity, blue/green enablement, and quick rollback. Keep old caches warm for one version overlap.
Context Drift Across Sessions
Why hard: Over time, session-level memory diverges from user intent or upstream data; agents start optimizing for outdated context.
Do this: Implement context expiry timestamps and freshness checks. Use delta-based updates (only write changed fields), and periodically rebuild context embeddings from authoritative sources.
Context Drift Across Sessions
Why hard: Over time, session-level memory diverges from user intent or upstream data; agents start optimizing for outdated context.
Do this: Implement context expiry timestamps and freshness checks. Use delta-based updates (only write changed fields), and periodically rebuild context embeddings from authoritative sources.
Context Drift Across Sessions
Why hard: Over time, session-level memory diverges from user intent or upstream data; agents start optimizing for outdated context.
Do this: Implement context expiry timestamps and freshness checks. Use delta-based updates (only write changed fields), and periodically rebuild context embeddings from authoritative sources.
Partial Failure Recovery
Why hard: One agent in a route fails or times out, but the orchestration retries the entire chain — wasting compute and creating duplicate outputs.
Do this: Add checkpointing between stages; retry failed agents in isolation with cached inputs; use idempotent message IDs to deduplicate outputs.
Partial Failure Recovery
Why hard: One agent in a route fails or times out, but the orchestration retries the entire chain — wasting compute and creating duplicate outputs.
Do this: Add checkpointing between stages; retry failed agents in isolation with cached inputs; use idempotent message IDs to deduplicate outputs.
Partial Failure Recovery
Why hard: One agent in a route fails or times out, but the orchestration retries the entire chain — wasting compute and creating duplicate outputs.
Do this: Add checkpointing between stages; retry failed agents in isolation with cached inputs; use idempotent message IDs to deduplicate outputs.
Latency Amplification in Nested Calls
Why hard: Agents that call other agents (e.g., “Research → Summarize → Validate”) multiply latency unpredictably, especially under load.
Do this: Instrument per-agent latency budgets, apply concurrency limits, and cache sub-agent outputs locally within the parent context.
Latency Amplification in Nested Calls
Why hard: Agents that call other agents (e.g., “Research → Summarize → Validate”) multiply latency unpredictably, especially under load.
Do this: Instrument per-agent latency budgets, apply concurrency limits, and cache sub-agent outputs locally within the parent context.
Latency Amplification in Nested Calls
Why hard: Agents that call other agents (e.g., “Research → Summarize → Validate”) multiply latency unpredictably, especially under load.
Do this: Instrument per-agent latency budgets, apply concurrency limits, and cache sub-agent outputs locally within the parent context.
Prompt Drift & Dependency Mismatch
Why hard: When prompts evolve separately from the templates or models they depend on, responses deviate subtly, breaking reproducibility.
Do this: Version-control prompts with explicit dependency metadata (model version, template hash). Run regression prompts in CI to detect semantic drift.
Prompt Drift & Dependency Mismatch
Why hard: When prompts evolve separately from the templates or models they depend on, responses deviate subtly, breaking reproducibility.
Do this: Version-control prompts with explicit dependency metadata (model version, template hash). Run regression prompts in CI to detect semantic drift.
Prompt Drift & Dependency Mismatch
Why hard: When prompts evolve separately from the templates or models they depend on, responses deviate subtly, breaking reproducibility.
Do this: Version-control prompts with explicit dependency metadata (model version, template hash). Run regression prompts in CI to detect semantic drift.
Cost Explosion under Adaptive Routing
Why hard: Adaptive routers may trigger multiple candidate agents “just to compare,” driving token and compute costs up exponentially.
Do this: Implement router confidence thresholds; if confidence > X, skip parallel evaluations. Log and review high-cost routes weekly.
Cost Explosion under Adaptive Routing
Why hard: Adaptive routers may trigger multiple candidate agents “just to compare,” driving token and compute costs up exponentially.
Do this: Implement router confidence thresholds; if confidence > X, skip parallel evaluations. Log and review high-cost routes weekly.
Cost Explosion under Adaptive Routing
Why hard: Adaptive routers may trigger multiple candidate agents “just to compare,” driving token and compute costs up exponentially.
Do this: Implement router confidence thresholds; if confidence > X, skip parallel evaluations. Log and review high-cost routes weekly.
Human Feedback Integration Loop
Why hard: Incorporating human-in-the-loop feedback mid-journey can desync the orchestrator’s internal state or cache validity.
Do this: Route human corrections through a feedback adapter that updates state and invalidates relevant cache keys. Track correction lineage to detect drift causes.
Human Feedback Integration Loop
Why hard: Incorporating human-in-the-loop feedback mid-journey can desync the orchestrator’s internal state or cache validity.
Do this: Route human corrections through a feedback adapter that updates state and invalidates relevant cache keys. Track correction lineage to detect drift causes.
Human Feedback Integration Loop
Why hard: Incorporating human-in-the-loop feedback mid-journey can desync the orchestrator’s internal state or cache validity.
Do this: Route human corrections through a feedback adapter that updates state and invalidates relevant cache keys. Track correction lineage to detect drift causes.
Evaluation Blind Spots
Why hard: Metrics like success rate or latency miss silent logical errors — e.g., plausible but wrong summaries.
Do this: Introduce semantic validators (LLM-based consistency checks or schema validation on outputs). Sample 1–2% of “successful” runs for deep audit comparison against ground truth.
Evaluation Blind Spots
Why hard: Metrics like success rate or latency miss silent logical errors — e.g., plausible but wrong summaries.
Do this: Introduce semantic validators (LLM-based consistency checks or schema validation on outputs). Sample 1–2% of “successful” runs for deep audit comparison against ground truth.
Evaluation Blind Spots
Why hard: Metrics like success rate or latency miss silent logical errors — e.g., plausible but wrong summaries.
Do this: Introduce semantic validators (LLM-based consistency checks or schema validation on outputs). Sample 1–2% of “successful” runs for deep audit comparison against ground truth.









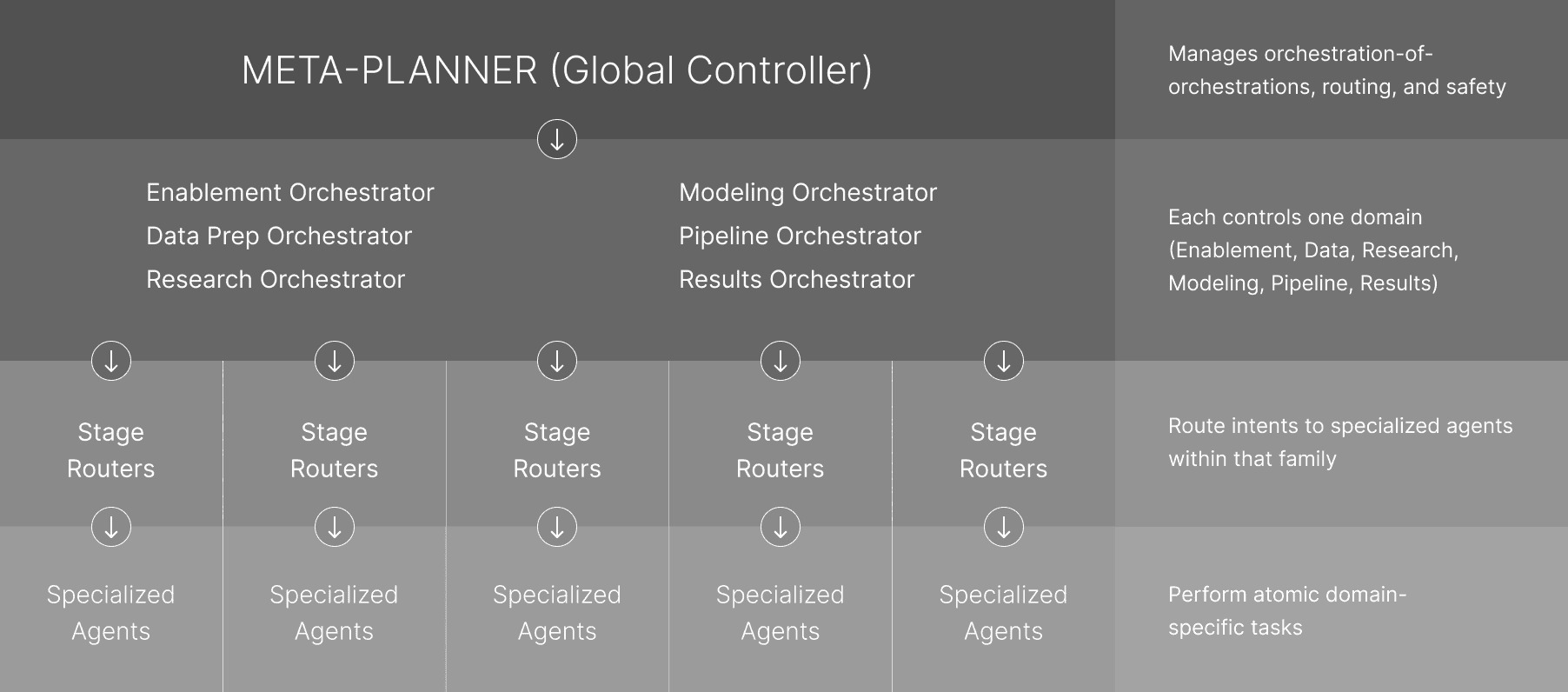


Why not “planner → agents” directly?
Separation of concerns:
Planner = global governance (budgets, recursion, cross-journey trade-offs).
Orchestrator = journey flow + state machine + retries + artifact handoffs.
Stage router = local choice of the best agent/prompt/tool for that stage.
Policy locality
Stage-specific guardrails (PII rules, cache TTLs, tool allowlists) live best near the stage. A global planner cannot safely encode hundreds of micro-policies without chaos.
Template reuse
Orchestrators package proven multi-step routes as templates. If the planner composes raw agents every time, you lose reuse, A/B testing, and versioning of flows.
Ownership & SLAs
Different teams own stages with distinct SLAs. Orchestrators bound latency/cost/retry for their family; the planner can’t maintain all those contracts cleanly.
Observability that matters
You want metrics per journey stage (hit/miss, p95, tokens saved). Routers/orchestrators emit these; a planner that calls agents directly gives you one big mushy trace.
Change safety
Change safety: Agents, prompts, models change often. Orchestrators/routers provide compatibility layers (schemas, adapters). Direct planner→agent coupling amplifies breakage.
Parallel evolution
You can swap a router or add a fallback agent without touching global logic. Tight planner→agent coupling forces global redeploys.
Separation of concerns:
Planner = global governance (budgets, recursion, cross-journey trade-offs).
Orchestrator = journey flow + state machine + retries + artifact handoffs.
Stage router = local choice of the best agent/prompt/tool for that stage.
Policy locality
Stage-specific guardrails (PII rules, cache TTLs, tool allowlists) live best near the stage. A global planner cannot safely encode hundreds of micro-policies without chaos.
Template reuse
Orchestrators package proven multi-step routes as templates. If the planner composes raw agents every time, you lose reuse, A/B testing, and versioning of flows.
Ownership & SLAs
Different teams own stages with distinct SLAs. Orchestrators bound latency/cost/retry for their family; the planner can’t maintain all those contracts cleanly.
Observability that matters
You want metrics per journey stage (hit/miss, p95, tokens saved). Routers/orchestrators emit these; a planner that calls agents directly gives you one big mushy trace.
Change safety
Change safety: Agents, prompts, models change often. Orchestrators/routers provide compatibility layers (schemas, adapters). Direct planner→agent coupling amplifies breakage.
Parallel evolution
You can swap a router or add a fallback agent without touching global logic. Tight planner→agent coupling forces global redeploys.
Separation of concerns:
Planner = global governance (budgets, recursion, cross-journey trade-offs).
Orchestrator = journey flow + state machine + retries + artifact handoffs.
Stage router = local choice of the best agent/prompt/tool for that stage.
Policy locality
Stage-specific guardrails (PII rules, cache TTLs, tool allowlists) live best near the stage. A global planner cannot safely encode hundreds of micro-policies without chaos.
Template reuse
Orchestrators package proven multi-step routes as templates. If the planner composes raw agents every time, you lose reuse, A/B testing, and versioning of flows.
Ownership & SLAs
Different teams own stages with distinct SLAs. Orchestrators bound latency/cost/retry for their family; the planner can’t maintain all those contracts cleanly.
Observability that matters
You want metrics per journey stage (hit/miss, p95, tokens saved). Routers/orchestrators emit these; a planner that calls agents directly gives you one big mushy trace.
Change safety
Change safety: Agents, prompts, models change often. Orchestrators/routers provide compatibility layers (schemas, adapters). Direct planner→agent coupling amplifies breakage.
Parallel evolution
You can swap a router or add a fallback agent without touching global logic. Tight planner→agent coupling forces global redeploys.















Beyond Template Promotion — Other Forms of Continuous Learning



metrics decomposition
metrics decomposition
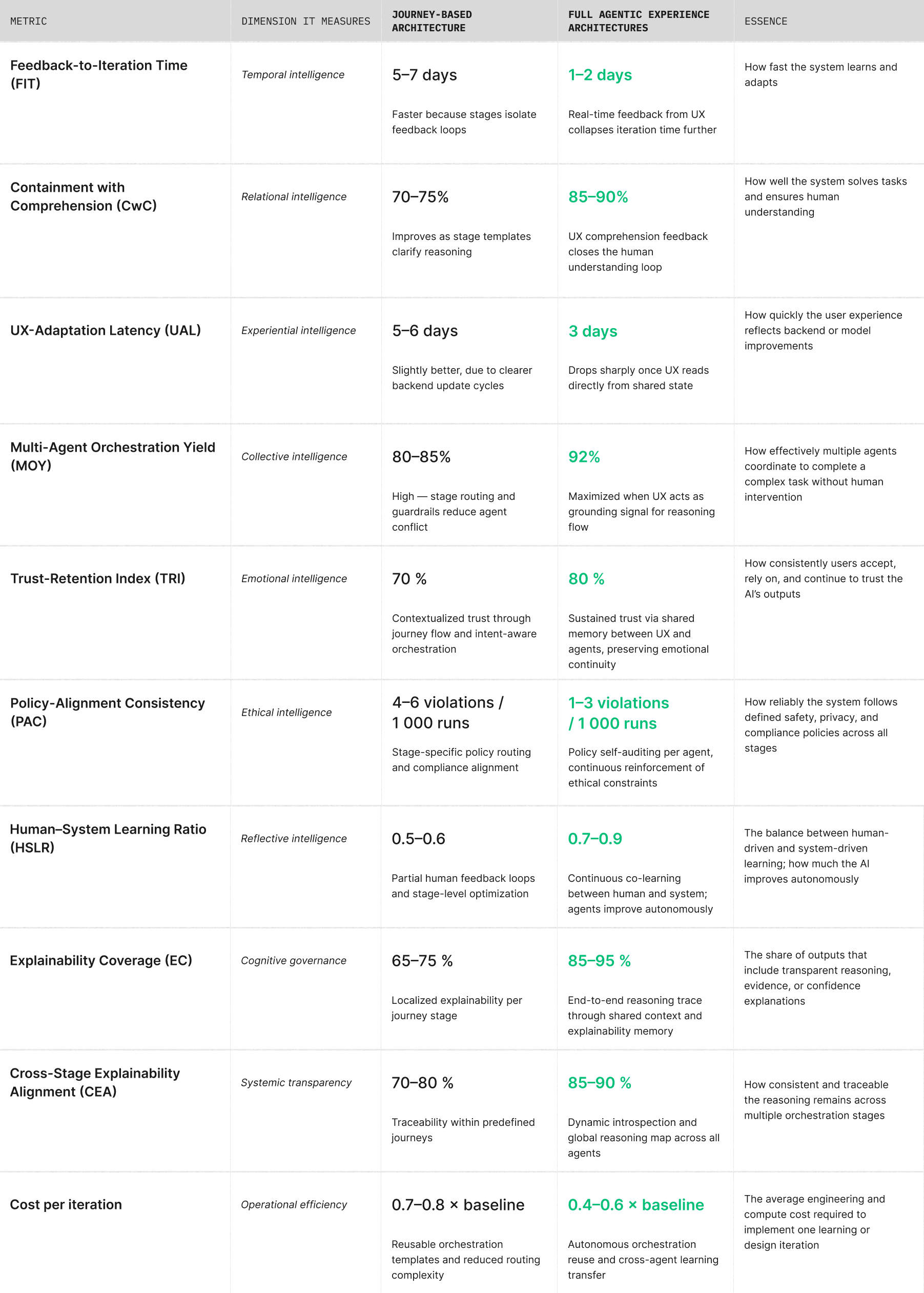
Measurable Gains from Journey-Based Design
Measurable Gains from Journey-Based Design



Performance Lift from Journey-Based to Fully Agentic Experience Architectures_1.1
Performance Lift from Journey-Based to Fully Agentic Experience Architectures_1.1


Continuous Learning Gets Easier
Continuous Learning Gets Easier
Continuous Learning Gets Easier
It becomes possible to see where and why behavior changes
Every interaction is tagged with its journey stage, allowing precise identification of reasoning or experience gaps
It becomes possible to see where and why behavior changes
Every interaction is tagged with its journey stage, allowing precise identification of reasoning or experience gaps
Learning focuses on what matters most
— Targeted data pipelines enable retraining or re-ranking only of underperforming stages (e.g., retrieval during Discover, rationale quality during Evaluate), avoiding full-system retraining
Learning focuses on what matters most
— Targeted data pipelines enable retraining or re-ranking only of underperforming stages (e.g., retrieval during Discover, rationale quality during Evaluate), avoiding full-system retraining
Iteration becomes safer and more controlled
Stage-scoped guardrails (PII, cost, or depth limits) contain risk, allowing independent experimentation without destabilizing the entire journey
Iteration becomes safer and more controlled
Stage-scoped guardrails (PII, cost, or depth limits) contain risk, allowing independent experimentation without destabilizing the entire journey
Success is clearly defined at each stage
Each step has an explicit definition of “done” (e.g., Evaluate = risks explained & accepted), producing stage-specific labels and higher-quality models
Success is clearly defined at each stage
Each step has an explicit definition of “done” (e.g., Evaluate = risks explained & accepted), producing stage-specific labels and higher-quality models
Patterns emerge through repetition, not redundancy
Stage-scoped guardrails (PII, cost, or depth limits) contain risk, allowing independent experimentation without destabilizing the entire journey
Patterns emerge through repetition, not redundancy
Stage-scoped guardrails (PII, cost, or depth limits) contain risk, allowing independent experimentation without destabilizing the entire journey
Feedback becomes inherently structured and reusable
— Because telemetry (UX signals, reasoning outcomes, policy events) is logged per stage, feedback loops form automatically, enabling the system to learn continuously from real interactions instead of manual labeling
Feedback becomes inherently structured and reusable
— Because telemetry (UX signals, reasoning outcomes, policy events) is logged per stage, feedback loops form automatically, enabling the system to learn continuously from real interactions instead of manual labeling
agent tuning gets easier
agent tuning gets easier
agent tuning gets easier
Narrower problem per agent
An agent owns a journey slice, not a vague job title. Narrow scope = clearer prompts, smaller RAG corpora, tighter evals
Narrower problem per agent
An agent owns a journey slice, not a vague job title. Narrow scope = clearer prompts, smaller RAG corpora, tighter evals
Composable improvements
If specific agent underperforms, you tune its explainer, not the whole system. Improvements don’t regress other stages
Composable improvements
If specific agent underperforms, you tune its explainer, not the whole system. Improvements don’t regress other stages
Shared telemetry across similar agents
Unified telemetry schema allows comparison across agents working within the same intent or stage, enabling meta-learning and faster generalization of improvements
Shared telemetry across similar agents
Unified telemetry schema allows comparison across agents working within the same intent or stage, enabling meta-learning and faster generalization of improvements
Targeted eval harnesses
You can build stage-specific tests (e.g., “explain trade-offs in ≤120 words with 2 citations”) and track CwC—Containment with Comprehension per stage
Targeted eval harnesses
You can build stage-specific tests (e.g., “explain trade-offs in ≤120 words with 2 citations”) and track CwC—Containment with Comprehension per stage
Prompt & policy libraries per stage
Reusable prompt blocks, critique rubrics, and policy checks aligned to that stage’s goal
Prompt & policy libraries per stage
Reusable prompt blocks, critique rubrics, and policy checks aligned to that stage’s goal
Stable evaluation baselines
Journey stages act as fixed reference frames for testing; identical datasets and policies ensure reproducibility and trustworthy longitudinal comparisons
Stable evaluation baselines
Journey stages act as fixed reference frames for testing; identical datasets and policies ensure reproducibility and trustworthy longitudinal comparisons
orchestration becomes easier
orchestration becomes easier
orchestration becomes easier
Intent-to-agent routing becomes obvious
Each journey stage maps to a small pool of eligible agents. Less guesswork, fewer misroutes
Intent-to-agent routing becomes obvious
Each journey stage maps to a small pool of eligible agents. Less guesswork, fewer misroutes
Clear prioritization
You can optimize the 20% of stages that handle 80% of traffic first
Clear prioritization
You can optimize the 20% of stages that handle 80% of traffic first
Better observability
Metrics roll up by journey stage (containment, turns-to-goal, latency per stage), so bottlenecks are easy to see
Better observability
Metrics roll up by journey stage (containment, turns-to-goal, latency per stage), so bottlenecks are easy to see
Reusable orchestration templates
Common paths become prebuilt graphs you can reuse across products
Reusable orchestration templates
Common paths become prebuilt graphs you can reuse across products
Cleaner guardrails
Policies attach to stages (e.g., stricter PII rules during Act), simplifying compliance
Cleaner guardrails
Policies attach to stages (e.g., stricter PII rules during Act), simplifying compliance
Cleaner guardrails
Policies attach to stages (e.g., stricter PII rules during Act), simplifying compliance
Cleaner guardrails
Policies attach to stages (e.g., stricter PII rules during Act), simplifying compliance
Featured AEA projects
More projects
More projects



Ready to start?
Get in touch
Whether you have questions or just want to explore options, I'm here.

Ready to start?
Get in touch
Whether you have questions or just want to explore options, I'm here.

Ready to start?
Get in touch
Whether you have questions or just want to explore options, I'm here.






